Demystifying Diabetes: Your First Step to Better Health
November is Diabetes Awareness Month. It’s time to learn more about a condition affecting millions of people. Do you have diabetes or wish to prevent it? Knowing the facts will help you take charge of your health.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a long-term condition that happens when your body doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it well. Insulin is a hormone that helps keep blood sugar (glucose) levels steady. When insulin isn’t doing its job, sugar can build up in the bloodstream. But the good news is that it can often be managed with the right steps.
There are three main types:
- Type 1: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks cells that make insulin. It’s often diagnosed in children and young adults.
- Type 2: The most common type. It often happens because of lifestyle factors, which make the body less able to use insulin. You can usually manage Type 2 with lifestyle changes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after childbirth. However, it may increase the risk of developing Type 2 later.
The Role of A1C
A1C, also known as hemoglobin A1C or HbA1C, is a critical blood test used to monitor and diagnose diabetes.
It measures the percentage of hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen) that is coated with sugar (glycated hemoglobin).
Here’s the role it plays in diabetes:
- Indicator of Average Blood Sugar Levels
- A1C reflects the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months. This timeframe corresponds to the lifespan of red blood cells.
- Unlike daily blood sugar tests, which capture a moment in time, A1C provides a broader picture of blood sugar control.
- Diagnosing Diabetes and Prediabetes
- Physicians use an A1C test to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes:
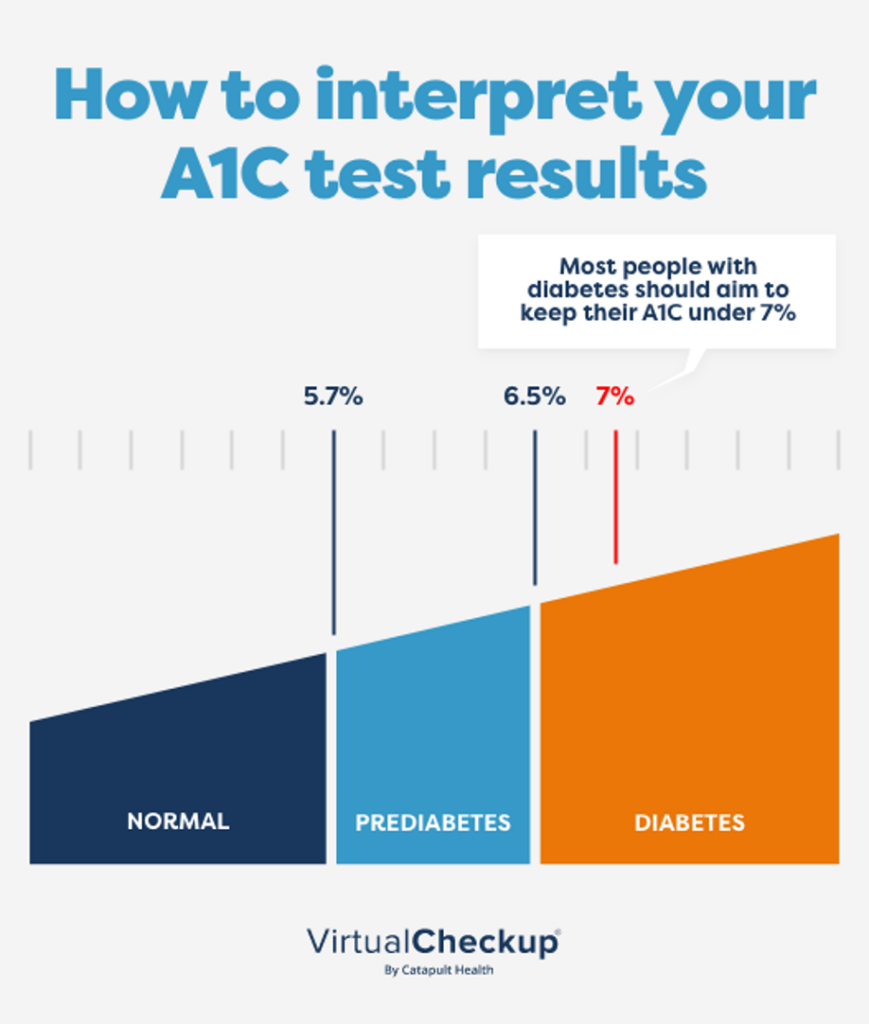
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher on two separate tests
- Physicians use an A1C test to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes:
- Monitoring Diabetes Management
- For people with diabetes, A1C helps determine how well their treatment plan is working.
- A typical goal for people with diabetes is an A1C below 7%, though targets can vary based on individual circumstances.
- Predicting Complications
- A higher A1C is associated with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications, such as:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney disease
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Eye problems (retinopathy)
- Keeping A1C levels within the recommended range can reduce these risks.
- A higher A1C is associated with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications, such as:
Why Is A1C Important?
A1C empowers patients and healthcare providers with critical insights into long-term blood sugar control, enabling adjustments to diet, exercise, medication, or insulin as needed. It’s a cornerstone for both prevention and effective management of diabetes.
Diabetes Prevention and Management
Preventing or managing diabetes starts with making healthy lifestyle choices. Eating a balanced diet is key—focus on whole foods like vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains, while cutting back on sugary drinks and processed foods. Regular physical activity, like walking, biking, or swimming, helps your body use insulin better and keep blood sugar in check. Aim for at least 30 minutes most days. Maintaining a healthy weight can also lower your risk of diabetes or make it easier to manage if you have it.
For people with diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels is essential. Follow your doctor’s advice on how often to check and what levels to aim for. Take medications or insulin as prescribed and keep up with regular A1C tests to understand your long-term blood sugar control. Small, steady changes to your daily habits can make a big difference in preventing complications.
Finally, focus on staying consistent. Managing stress, getting enough sleep, and building a support system can help you stick to your plan. Talk to your doctor for personalized advice—they’re there to help you succeed.
GLP-1 Medications and Managing Diabetes
GLP-1 drugs, or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, help people with diabetes by improving blood sugar control and supporting weight management. These medications mimic a natural hormone in the body that helps regulate blood sugar after eating. They encourage the pancreas to release insulin when blood sugar levels are high and reduce the amount of sugar the liver makes.
Another important benefit is that GLP-1 drugs can slow down how quickly food leaves the stomach. This helps prevent blood sugar spikes and may make people feel fuller for longer, which can support weight loss. Since excess weight can make diabetes harder to manage, losing weight often improves overall blood sugar control.
Think of GLP-1 medications as a tool to enhance your efforts. They make managing diabetes easier, but the foundation for success is still a healthy lifestyle. They are typically used alongside a healthy diet, exercise, and other diabetes treatments as recommended by a healthcare provider. Together, they create the best chance for long-term health and improved quality of life.
How Catapult’s VirtualCheckup Can Help?
Catapult Health’s VirtualCheckup helps people better understand their health by providing clear, personalized insights, including an A1C test that measures average blood sugar levels. This test can identify whether you’re at risk for diabetes, already living with it, or managing it well, empowering you to act based on your results.
Our nurse practitioners take the time to explain what your numbers mean and discuss simple lifestyle changes that can make a big difference in lowering your A1C. They often recommend programs covered by your employer or insurance—like weight management, nutrition counseling, or diabetes education—designed to help you manage diabetes effectively, often at no cost to you.
By providing both the information and the tools to act on it, VirtualCheckup supports better health and gives you the confidence to take control of your well-being.
Taking steps to understand your health today can lead to a healthier future.